
남자는 허리

척수의 구조
척수는 기본적인 분절 조직을 유지하는 길고 가느다란 신경 조직의 원통형 구조로, 분절의 수는 종에 따라 다르다.
인간의 척수 신경(31쌍)
- Cervical(경추 신경) : 8쌍
- Thoracic(흉추 신경) : 12쌍
- Lumbar(요추 신경) : 5쌍
- Sacral(천추 신경) : 5쌍
- Coccygeal(미추 신경) : 1쌍
척수의 확장
- 척수는 첫 번째 또는 두 번째 요추 수준까지 확장
- 두 번째 요추 수준 그 이하의 부분은 Cauda equina(말총)



1. White matter(백질)
- 백질은 신경 섬유 다발(tracts)로 구성
- 수초가 있는 신경 섬유로 이루어졌다.
- Ascending tracts(상행로) : Afferent impulses(구심성 신호)를 뇌로 전달
- Descending tracts(하행로) : 뇌에서 Efferent neuron으로 Efferent impulses(원심성 신호) 메시지로 전달
2. Gray matter(회백질)
- 밀집된 세포체와 신경교세포로 이루어졌다.
- 신경 입력을 통합하고 신경 출력을 시작(Synapse)
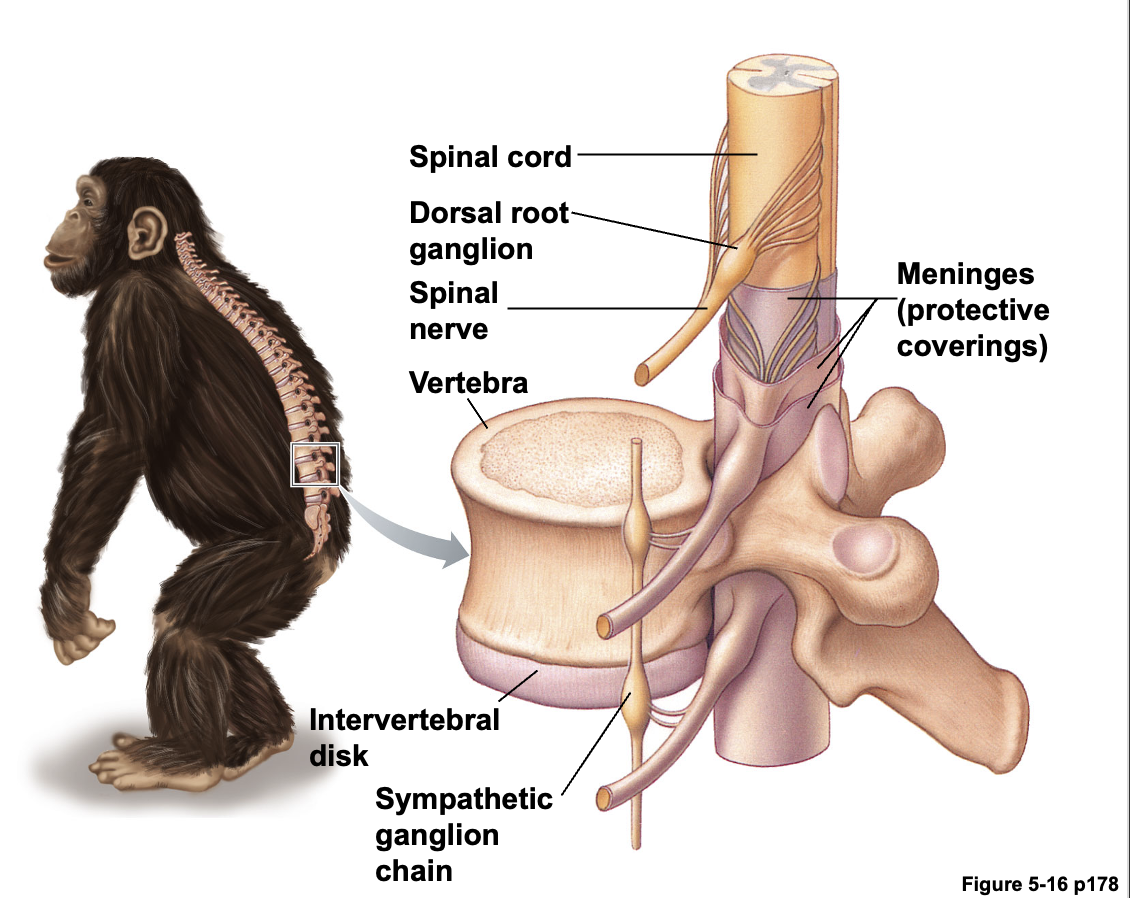
Spinal nerves(척수 신경) : Afferent fiber와 Efferent fiber가 결합 조직에 둘러싸여 있다.
- Afferent fibers :
구심성 섬유는 척수의 배근(Dorsal root)을 통해 척수에 들어간다. Afferent neurons의 세포체는 배근 신경절(Dorsal root ganglion)에 모여 있다.
- Efferent fibers :
원심성 섬유는 척수의 복근(Ventral root)을 통해 척수를 떠난다. Efferent neurons의 세포체는 gray matter에 위치.
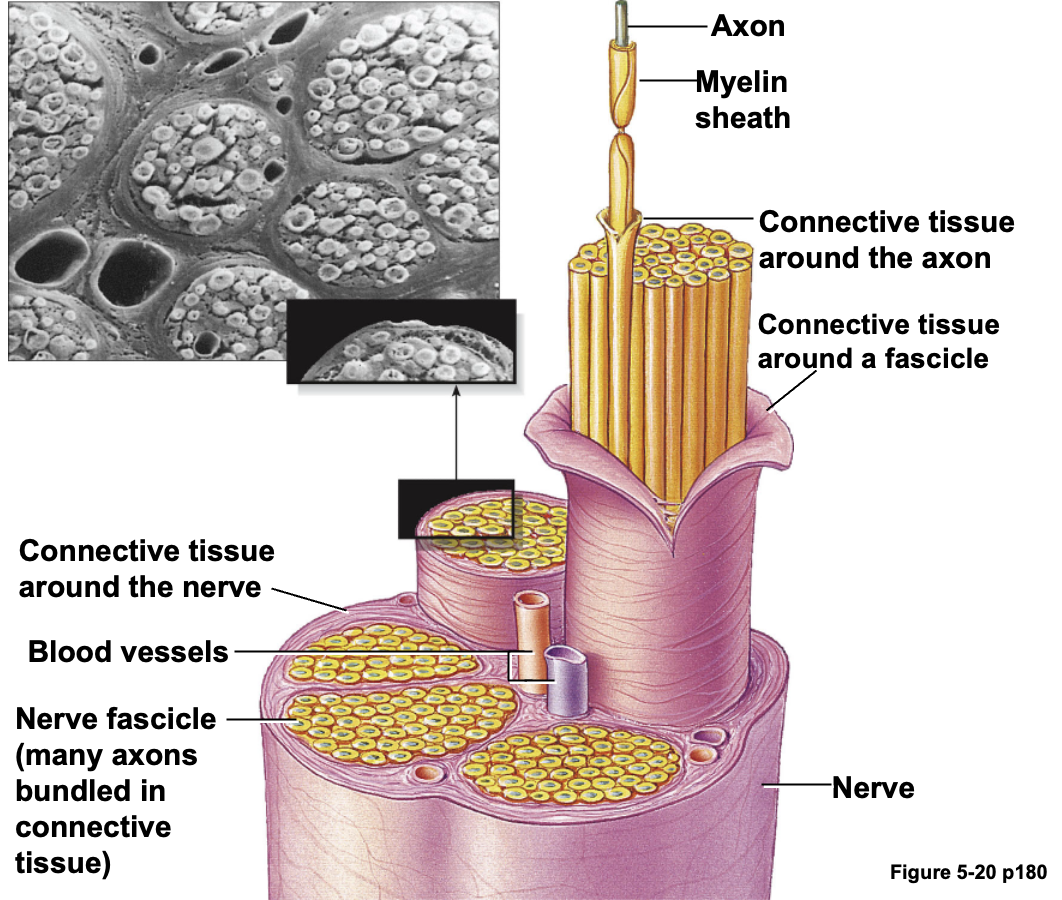
Nerve(신경) :
- 신경은 말초 신경 축삭 다발로 이루어져 있다.
- 신경은 완전한 신경 세포를 포함하지 않으며, 축삭만 포함된다.
- CNS에서 축삭 다발은 'tracts' 라고 불린다.
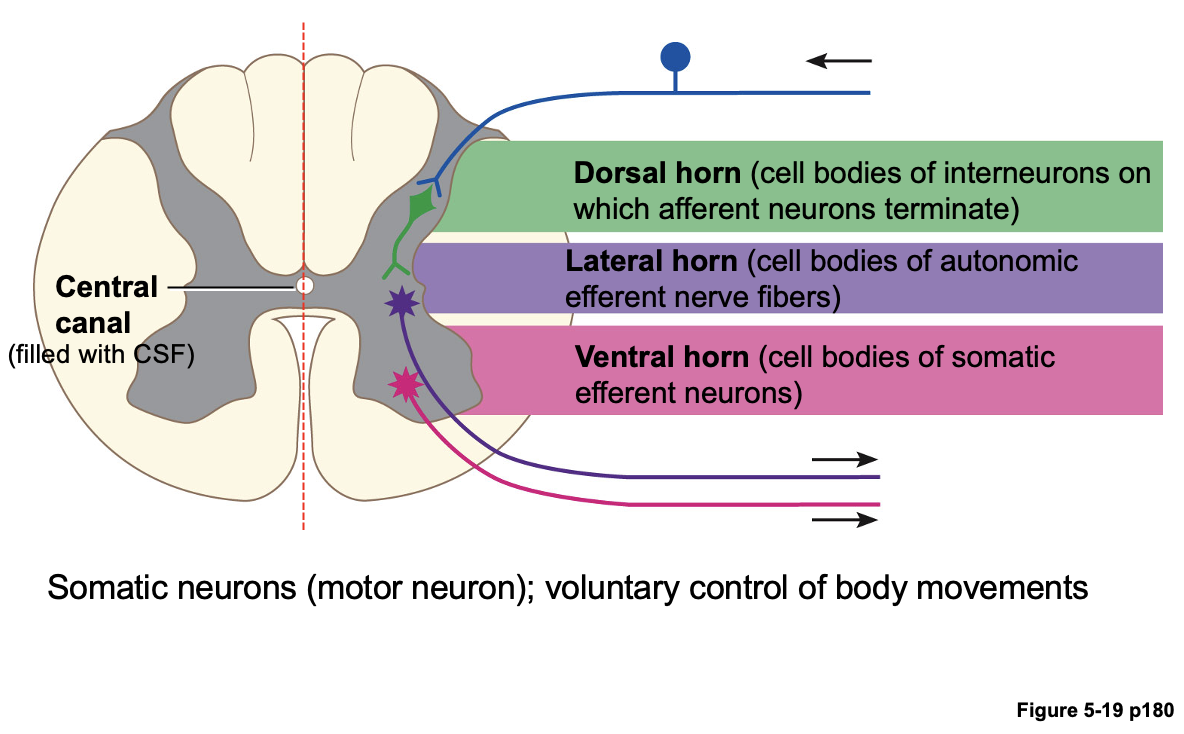
척수 회백질의 각 뿔(horn)은 다른 유형의 신경 세포체를 포함하고 있다.
- 배측 뿔(Dorsal horn) : Afferent neuron이 종결되는 interneurons의 세포체를 포함
- 복측 뿔(Ventral horn) : Efferent motor neurons의 세포체를 포함
- 측면 뿔(Lateral horn) : Automatic neurons(자율 신경 뉴런)의 세포체를 포함
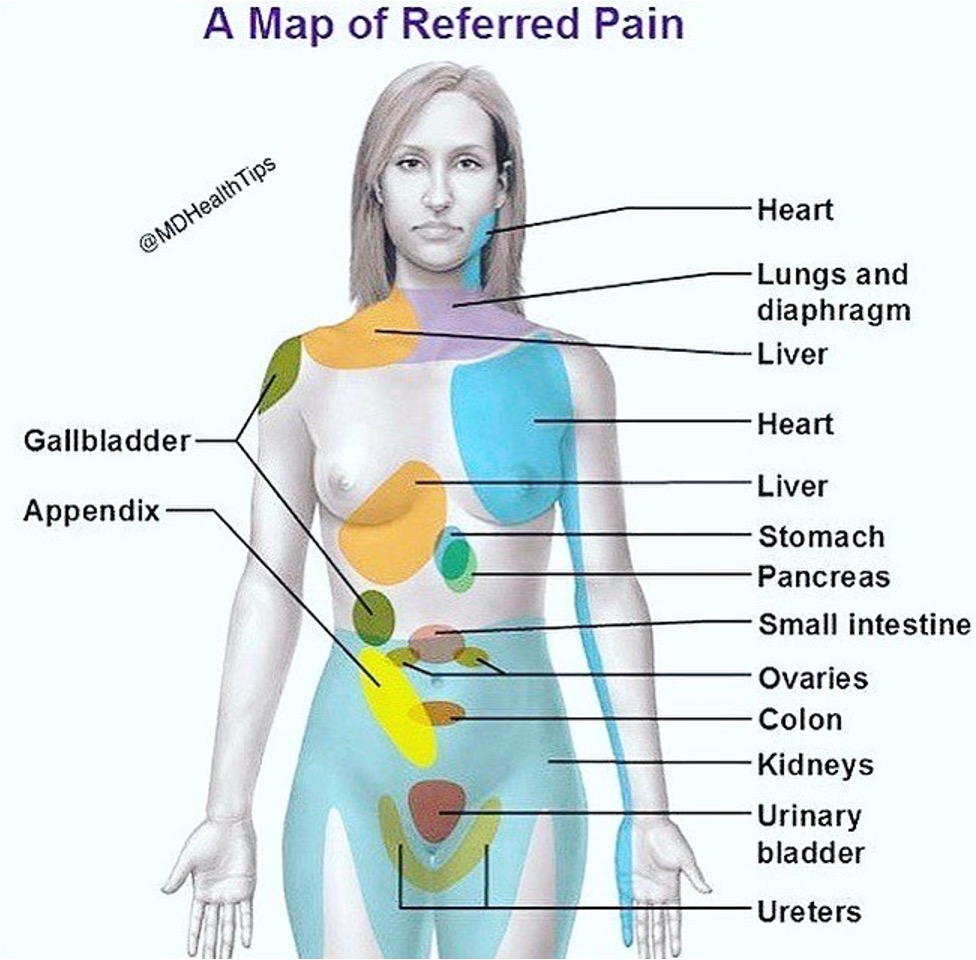
Spinal nerves contain both afferent and efferent fibers enclosed in connective tissue. Each region of the body surface, supplied by a particular spinal nerve, is called a dermatome (sensory input). Referred pain; pains originated from heart dermatome, but the pains appeared to come from upper extremities – those different tissues supplied by the same spinal nerve.
- Spinal nerves(척수 신경) : 척수 신경은 결합 조직에 둘러싸인 afferent fibers와 efferent fibers를 포함
- Dermatome(피부 분절) : 특정 척수 신경에 의해 공급되는 신체 표면의 각 영역. 감각 입력과 관련된다.
- Referred pain(관련통) : 심장에서 유래한 통증이 상지에서 오는 것처럼 느껴지는 현상. 서로 다른 조직이 동일한 척수 신경에 의해 공급될 때 발생.
Reflex 반사
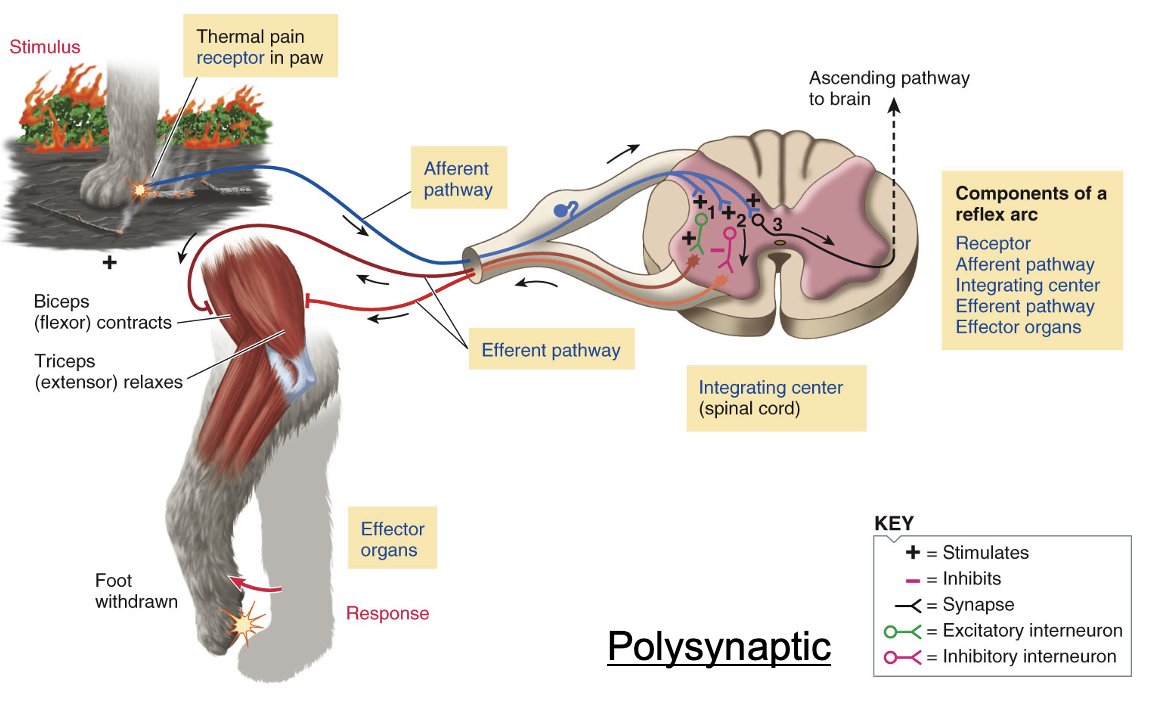
Many reflex responses and patterned movements in vertebrates are integrated in the spinal cord
Function of spinal cord :Transmits information between the brain and the body. Integrates reflex activity between afferent input and efferent output w/o involving brain (spinal reflex)
Ex. Beheaded chicken still walk for a while
Reflex is an innate response (pulling a limb away from hot object)
Some true reflex can be acquired by improving potentiated synapses -> acquired reflex
Spinal cord and brainstem; basic reflex
Many reflex responses and patterned movements in vertebrates are integrated in the spinal cord.
Withdrawal reflex
Withdrawal of a limb from a painful stimulus
CNS must distinguish various stimuli -> different afferent pathways are activated by different stimuli (stronger the stimuli, greater the frequency of action potentials)
Excited afferent neurons stimulate excitatory interneurons that stimulate efferent motor neurons to flexor muscles (polysynaptic reflex)
Afferent neurons also stimulate inhibitory interneurons that inhibit efferent neurons supplying extensor muscles (reciprocal innervation; One is stimulated while the other is inhibited)
Other interneurons ascend the signal to a sensory area of the brain -> can be stored as memory
척수의 기능
뇌와 몸 사이의 정보를 전달. 반사 활동을 통합한다(Afferent input과 efferent output을 통합하여 뇌를 거치지 않고 반사 활동을 수행, 척수 반사)
ex) 목이 잘린 닭이 잠시 동안 걸을 수 있다.
반사 반응
선천적 반응 : 반사는 선천적인 반응(innate response)
ex) 뜨거운 물체에서 팔다리를 당기는 것
습득된 반사 : 일부 반사는 강화된 시냅스를 통해 습득될 수 있다.
기본 반사 : Spinal cord와 brainstem
Withdrawal Reflex 회피 반사
고통스러운 자극으로부터 팔다리를 회피하는 반사
중추신경계에서 다양한 자극을 구별하여 서로 다른 구심성 경로를 활성화(자극이 강할수록 활동 전위와 빈도가 증가)
Polysynaptic reflex(다중 시냅스 반사)
- Excited interneurons : 흥분된 구심성 뉴런이 흥분성 중간 뉴련을 자극하여 flexor muscles(굴근)의 원심성 운동 뉴런 자극
- Inhibitory interneurons : 구심성 뉴련이 억제성 중간 뉴런을 자극하여 extensor muscles(신전근)을 공급하는 원심성 뉴런을 억제
* Reciprocal innervation(상호 신경 지배) : 하나가 자극되면 다른 하나는 억제된다.
- 다른 중간 뉴런이 신호를 뇌의 감각 영역으로 전달하여 기억으로 저장될 수 있다.
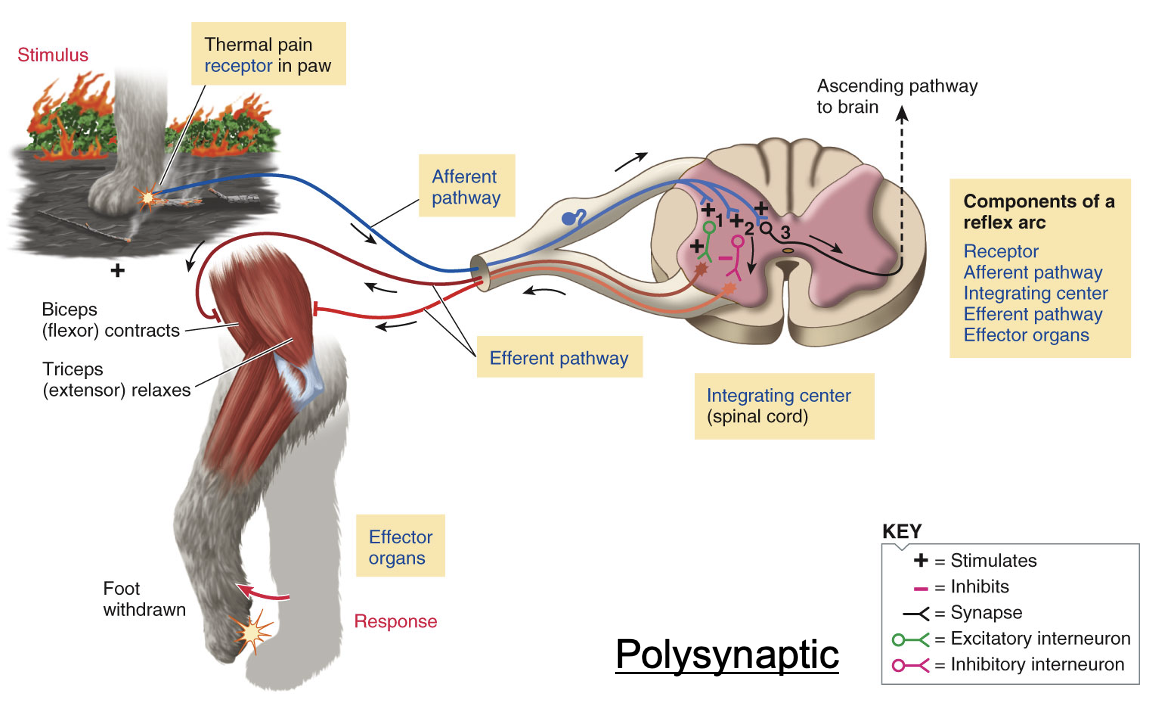
Stretch reflex; simpler than withdrawal reflex
Skeletal muscle contracts to counteract a stretch stimulus
Stretch in skeletal muscle -> afferent neuron terminates directly on the efferent neuron -> same skeletal muscle became contracted
Afferent neuron originating stretch-detecting receptor in the muscle synapses directly on efferent neuron (monosynaptic)
-- No interneuron is involved
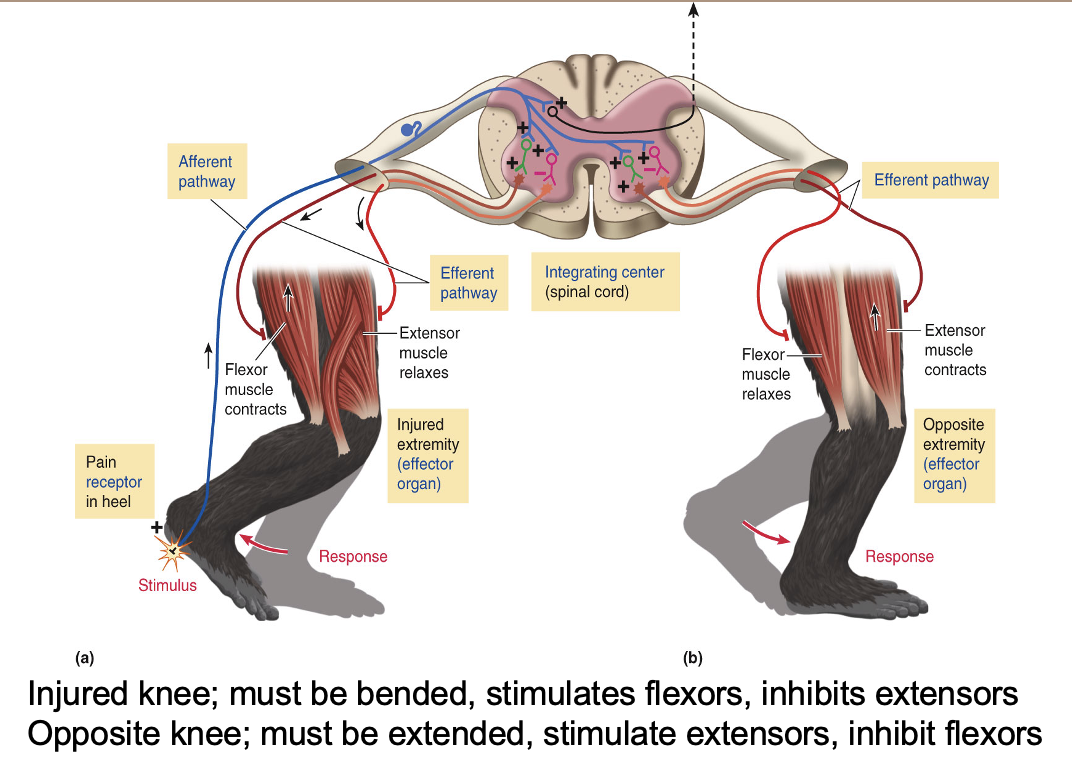
Crossed extensor reflex
Extension of the opposite limb during the withdrawal reflex
Ensures that opposing limb will be in position to bear weight when the injured limb is withdrawn to make balance of body
Reflexes and higher regulation
Anticipation
Suppression
Ex) During feeding breast milk to the lovely baby
- In normal condition; bite mother’s nipple -> pain occurs -> initiates withdrawal reflex
- During feeding; IPSPs via descending pathways to the motor neurons, that is, IPSPs from the brain (non-reflex) override the EPSPs from the afferent pain pathway (reflex)
Activity of command fibers elicits a fixed action pattern
Activation of certain command fibers (ex. Mauthner neurons) located within CNS generates innately fixed action patterns (stereotyped behaviors) - automatic and innate
Ex) mating dances, escape responses, molting
Mauthner neurons generate startle response -> vigorous muscle contraction on one side of the body
Ecdysis behavior
Peristaltic movements of muscles from posterior to anterior
Stretch reflex(신전 반사)
신전 자극에 대응하여 골격근이 수축
Monosynaptic Reflex : 단일 시냅스 반사. 골격근의 신전에서 시작된 afferent neurons이 efferent neurons과 직접 synapse를 형성하여 같은 골격근이 수축
ex) 근육 내 신전 감지 수용체에서 시작된 afferent neurons이 efferent neurons과 직접 시냅스를 형성하여 근육이 수축(Interneuron은 관여하지 않음)
Crossed Extensor Reflex(교차 신전 반사)
회피 반사 동안 반대쪽 팔다리의 신전
부상당한 팔다리를 제거할 때 몸의 균형을 유지하기 위해 반대쪽 팔다리가 체중을 지탱할 수 있도록 한다.
반사 조절
Anticipation, Suppression
ex) 사랑스러운 아기에게 모유를 먹일 때
일반적인 상황에서는 엄마의 젖꼭지를 물면 통증이 발생하여 회피 반사가 시작된다.
수유 중일 때, 하행 경로를 통한 IPSPs(억제성 시냅스 후 전위)로 인해 비반사적인 뇌의 IPSPs가 구심성 통증 경로의 EPSPs(흥분성 시냅스 후 전위)를 억제한다.
Command fibers 명령 섬유
중추 신경계 내 특정 명령 섬유(ex. Mauthner neuron)의 활성화는 선천적으로 고정된 행동 패턴을 생성(자동적이고 선천적인 행동)
Ex. Mating dances(짝짓기 춤), Escape responses(도피 반응), Molting(탈피)
Molting(탈피)
- Mauthner Neurons : 놀람 반응을 생성하여 신체의 한쪽에서 강한 근육 수축을 유발
- Ecdysis behavior(탈피 행동)
- Peristaltic movements(연동 운동) : 후방에서 전방으로 근육의 연동 운동

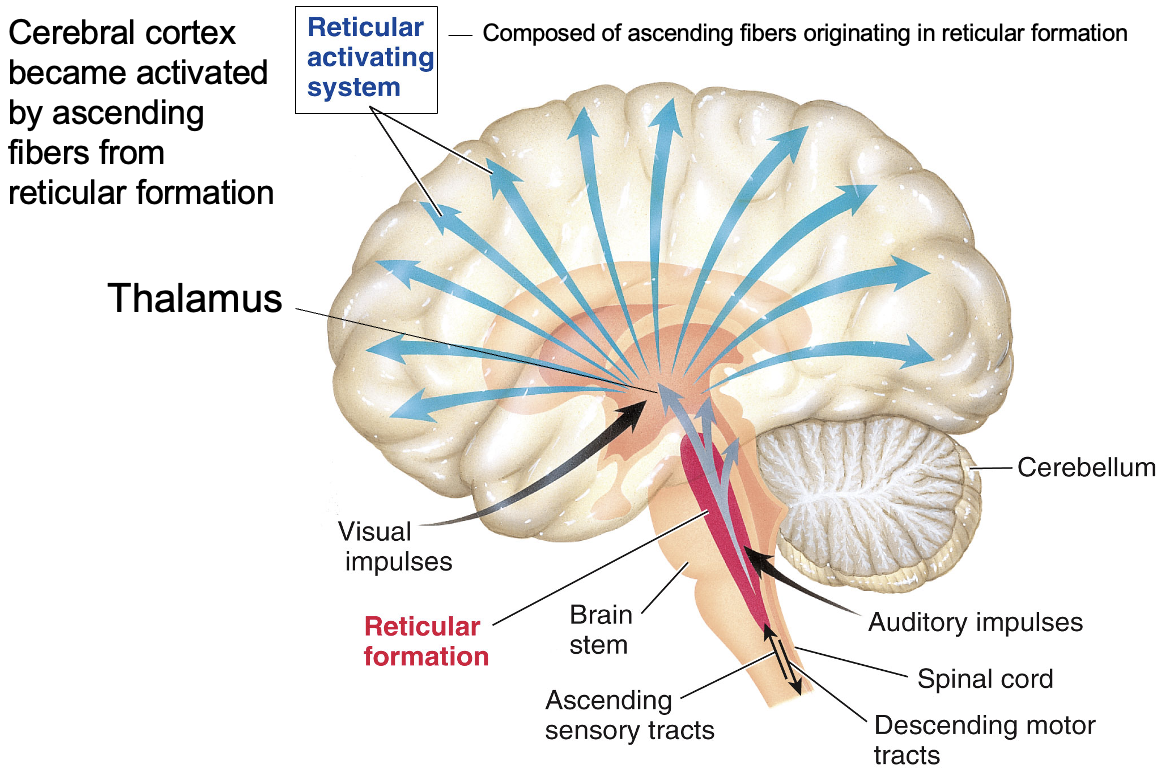
Brainstem; critical connecting link between brain and spinal cord
Almost all the incoming and outgoing fibers pass through the brainstem
Functions : Sensation input and motor output in the head and neck via 12 pairs of cranial nerves (Fig. 5-7) – cranial nerve X; vagus nerve
Reflex control of heart, blood vessels, respiration and digestion (pon and medula)
Modulation of pain sensation
Regulation of muscle reflexes involved in equilibrium and posture
Control the level of cortical alertness via the reticular activating system (Fig. 5-23)
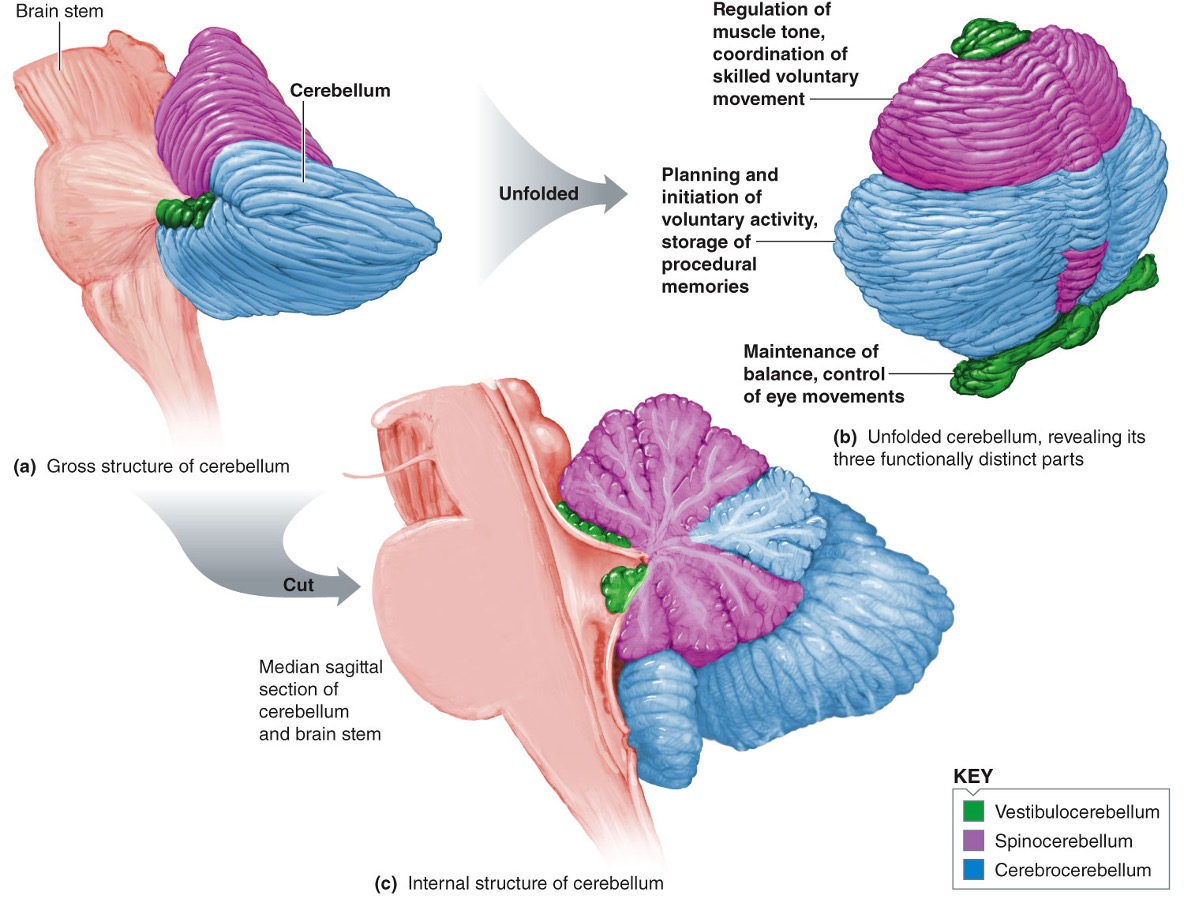
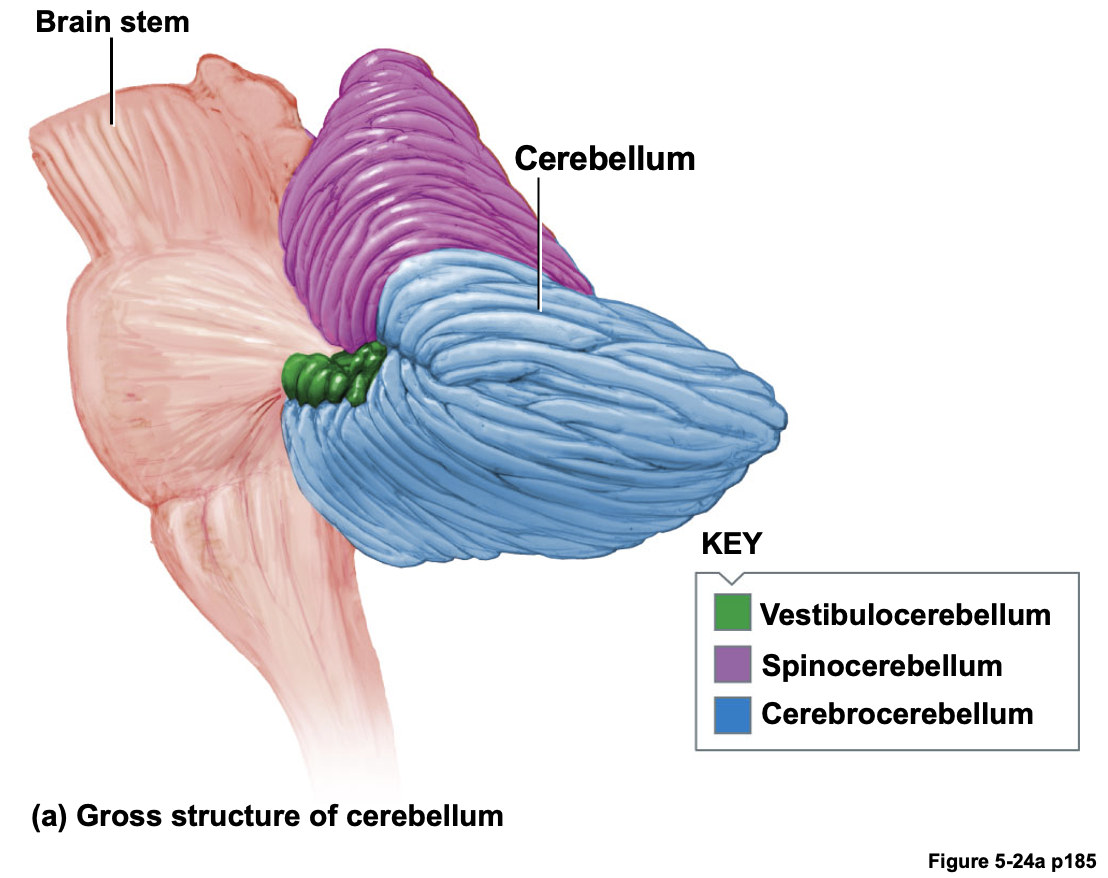
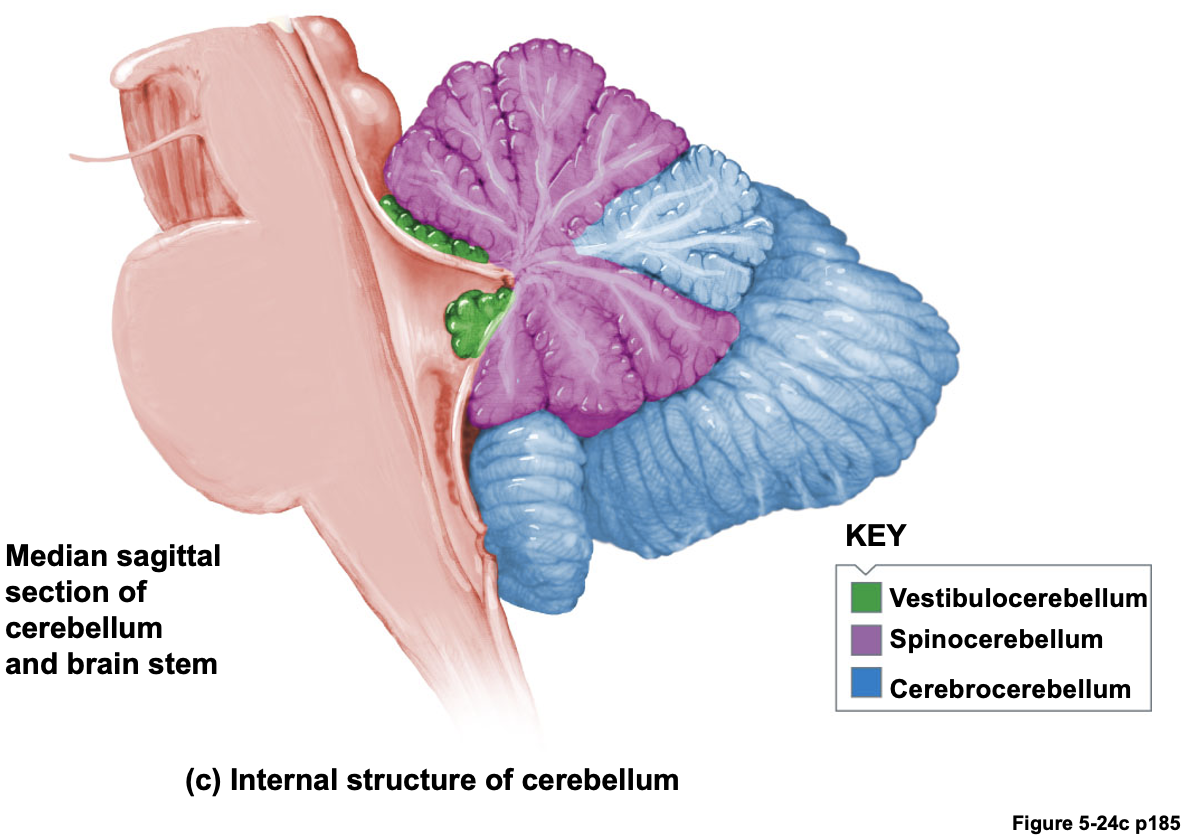
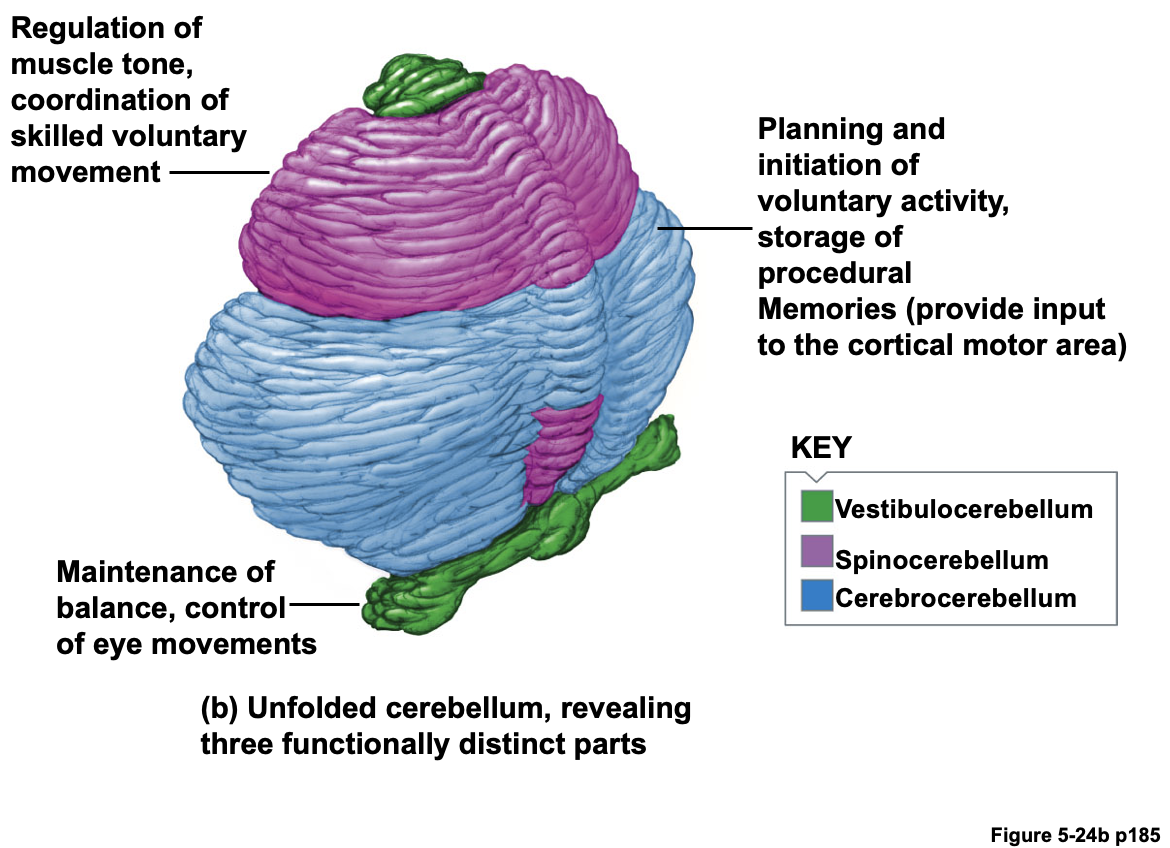
Responsible to sleep (also the hypothalamus is involved in slow wave sleep)Cerebellum (Fig. 5-24)
Important in balance and coordination (main motor activity controlling region)
Three parts have different sets of inputs and outputs
Vestibulocerebellum -- maintains balance and controls eye movements
Cerebrocerebellum -- voluntary muscle activity (nonreflex muscle activity) by providing input to the cortical motor areas. Procedural memory.
Spinocerebellum -- enhances muscle tone and coordinates skilled, nonreflex movements; ensuring the accurate timing of various muscle contractions for the coordinated movements. Ex – When you pick up the fragile but expensive glasses
- Also acting as a middle manager to correct errors of the muscle movements
- Compare orders from motor cortex (cerebral cortex) with performance (muscles) -> correct errors
Reticular Activating system 망상 활성화 시스템
상행 섬유 : Reticular formation(망상 형성)에서 기원한 상행 섬유로 대뇌 피질을 활성화
Brainstem과 spinal cord의 역할 : 시각, 청각 및 감각 신호를 전달
Cerebral cortex는 reticular formation에서 기원한 상행 섬유에 의해 활성화
Thalamus : 감각 정보를 필터링하고 우선순위를 정하여 마음이 경계하고 깨어있도록 각성
Brainstem 뇌간
Brain과 spinal cord 사이의 중요한 링크
거의 모든 들어오거나 나가는 섬유가 brainstem을 통과, 신경 섬유의 통로가 된다.
12쌍의 cranial nerves(뇌신경)을 통해 머리와 목에서 감각 입력과 운동 출력을 조절
Pons와 Medulla obiongata에서 심장, 혈관, 호흡 및 소화의 반사적 제어 담당
통증 감각을 조절
근육 반사를 조절 - 평형과 자세 유지에 관련된 근육 반사 조절
RAS를 통해 대뇌 경계 수준을 조절
수면에 관여 - hypothalamus도 느린 파수면에 관여
Cerebellum 소뇌
균형과 조정에 중요한 역할 수행 - 주요 운동 활동 제어 영역
Vestibulocerebellum : 전정 소뇌. 균형 유지 및 안구 운동 조절
Cerebrocerebellum : 대뇌 소뇌. 자발적 근육 활동(비반사 근육 활동)을 담당하고 cerebral cortex 운동 영역에 입력 제공. Procedural memory(자전거 타기 등)에 관여.
Spinocerebellum : 척수 소뇌. 근육 긴장 강화. 숙련된 비반사 운동의 조정, 다양한 근육 수축의 정확한 타이밍 보장. 운동 오류 수정 역할(중간 관리자로서 근육 움직임의 오류를 수정하고, 대뇌 피질에서 명령을 받아 수행 결과와 비교하여 오류를 수정)
Motor commend for a particular nonreflex activity arises from the motor cortex. The coordination of the actual execution of the motor activity is accomplished by the cerebellum and other subcortical regions
특정 비반사 활동에 대한 운동 명령은 mortor cortex에서 발생한다. 실제 운동 활동의 실행 조정은 cerebellum 및 기타 피질하 영역(subcortical regions)에 의해 이루어진다.
Motor cortex : 비반사적인 운동활동(의식적으로 제어되는 움직임)에 대한 명령이 motor cortex에서 시작된다. 즉, 우리가 의식적으로 팔을 들어올리거나 걷는 것과 같은 행동을 하려면, 이러한 명령은 motor cortex에서 발생한다.
Cerebellum 또는 Subcortical regions : 이러한 명령이 실제로 실행되기 위해서는 운동의 조정이 필요하다. Cerebellum과 subcortical regions는 운동의 실제 실행을 조정하여 동작이 부드럽고 정확하게 이루어지도록 한다. 예를 들면, motor cortex가 팔을 들으라는 명령을 내리면, cerebellum은 그 팔을 정확한 높이와 속도로 들어올리도록 조정한다.
다시 말하면, Motor cortex은 행동에 대한 전체적인 guide line, cerebellum과 subcortical regions는 디테일.
Basal nuclei(Basal ganlia) 기저핵
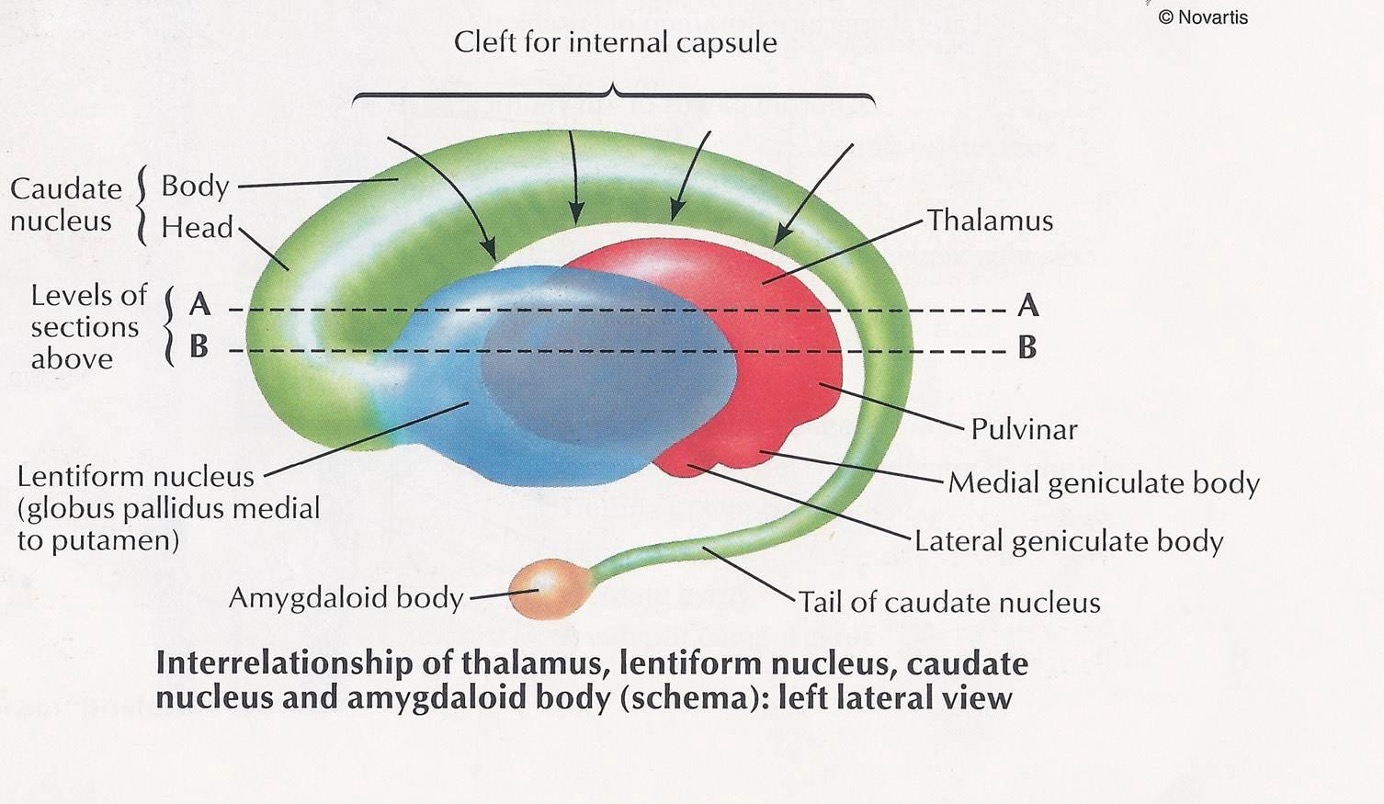
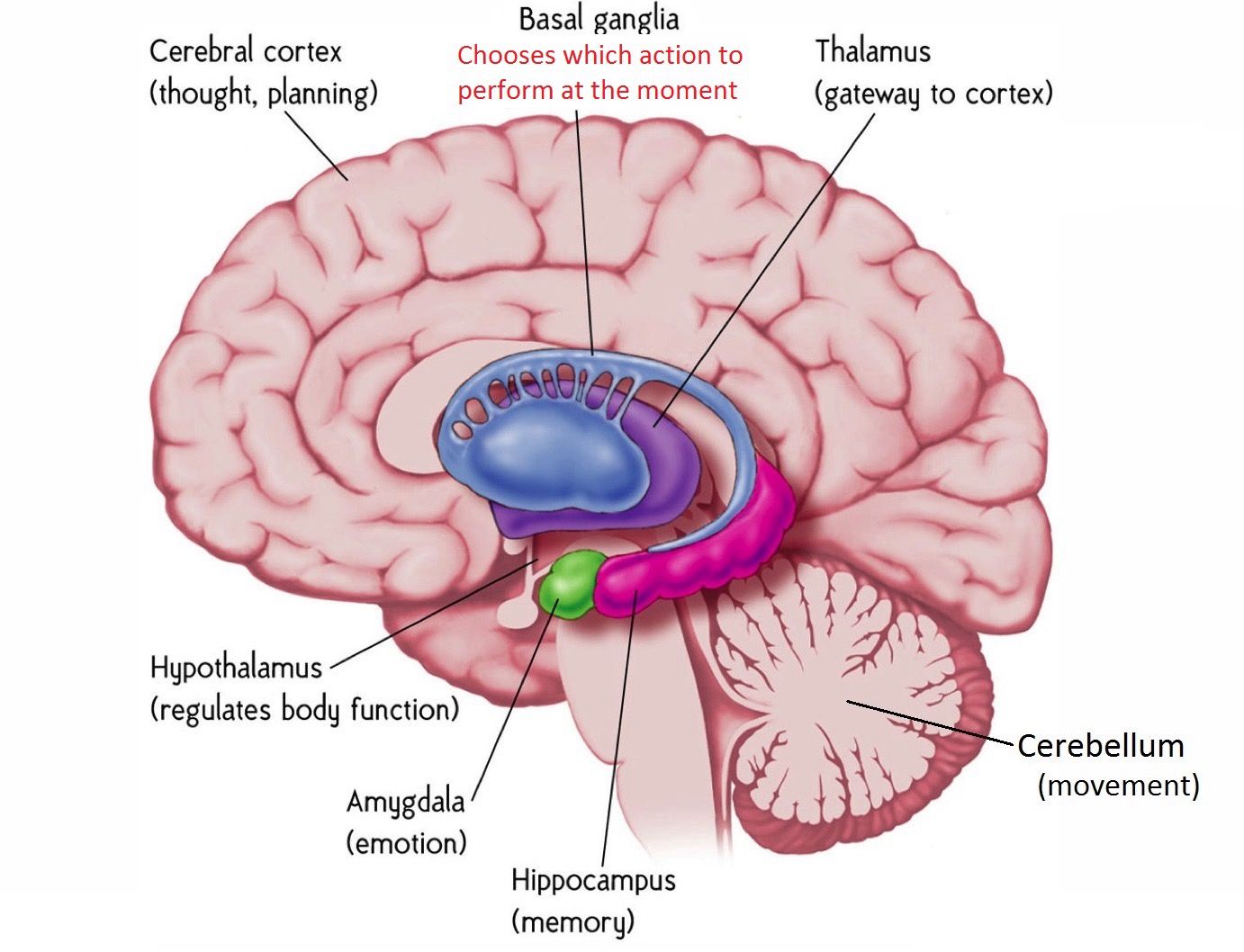
Subcortical (under the cortex) regions
- basal nuclei; located in cerebrum
- thalamus, hypothalamus; diencephalon
- limbic system; some portion of cerebral cortex diencephalon and basal nuclei
Basal nuclei (basal ganglia)
Nucleus in nervous system stands for the functional aggregation of neuronal cell bodies
Masses of gray matter deep within the cerebrum
Functions
Inhibit muscle tone
Select and maintain purposeful motor activity, while suppressing unwanted movements
Monitor and coordinate slow, sustained contractions related to posture and support
Similar to the cerebellum, the basal nuclei do not have any direct influence on the efferent motor neurons just modulating the output of major motor systems of brain
Basal nuclei (basal ganglia)
Motor cortex -> thalamus positively reinforces nonreflex motor behavior whereas basal nuclei exerts inhibitory effects on thalamus -> eliminate unnecessary movements
The basal nuclei and cerebellum both monitor and adjust motor activity commanded from the cerebral cortex (motor cortex)
Basal nuclei, cerebellum; Do not directly influence but modulate the efferent motor neurons
Cerebellum; helps coordinate fast movement, phasic motor activity, enhances muscle tone (excitatory input)
Basal nuclei; helps coordinate slow and sustained movement, inhibits muscle tone (inhibitory input)
Hypothalamus
Integrating center for homeostatic functions
Body temperature (Ex. Shivering)
Thirst and urine output
Food intake (Alzheimer’s disease)
Controls anterior pituitary hormone secretion
Produces posterior pituitary hormones
Stimulate uterine contraction and milk ejection
Autonomic nervous system coordination, as influences all smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, exocrine glands
Emotional and behavioral patterns
Sleep-wake cycle (circadian rhythm); together with pineal gland
Hypothalamus is a intermediate reflex integrator. It can receive input and send out commends without help of cerebrum (but less)
Subcortical regions 피질하 영역
- Basal Nuclei : 기저핵, cerebrum에 존재
- Thalamus, Hypothalamus : 시상, 시상하부. Diencephalon에 위치
- Limbic system : 변연계. Cerebral cortex의 일부와 diencephalon의 일부로 구성
Basal nuclei
Neuron systems의 핵은 neuronal cell bodies(신경 세포체)의 기능적 집합체를 의미한다. Cerebrum 깊숙히 위치한 회백질 덩어리.
- 근육 긴장 억제
- 목적 있는 운동 활동 선택 및 유지, 원치 않는 움직임 억제
- 자세와 지지를 위한 느리고 지속적인 수축 조정
- Cerebral cortex의 운동 명령을 모니터링하고 조정
- Motor neuron에 직접 영향을 미치지 않으며, 주요 운동 시스템의 출력을 조절하는 역할 수행
Thalamus
- 모든 감각 입력의 예비 처리를 위한 시냅스 통합 센터
- 무의미한 감각 입력을 걸러내고 중요한 자극에 주의를 기울이도록 함
- Cerebrum cortex에서의 비반사적 운동 행동 강화
- 흥미로운 자극에 주의를 집중시키는 역할
Hypothalamus
- Homeostasis 유지의 중심
- 체온 조절, 갈증 및 소변 배출 조절, 음식 섭취 조절
- Anterior pituitary 호르몬 분비 조절
- Posterior pituitary 호르몬 생성 및 uterine contraction(자궁 수축)과 milk ejection(유즙 분비 자극)
- Automatic nervous system 조정 : all smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, exocrine glands에 영향
- 감정 및 행동 패턴 조정
- 수면-각성 주기 조절 : Pineal gland와 함께 Circadian rhythm(일주기 리듬) 조절
- 중간 반사 통합체로서 입력을 받고 명령을 보낼 수 있음(Cerebrum의 도움 없이도 가능하지만 덜하다)
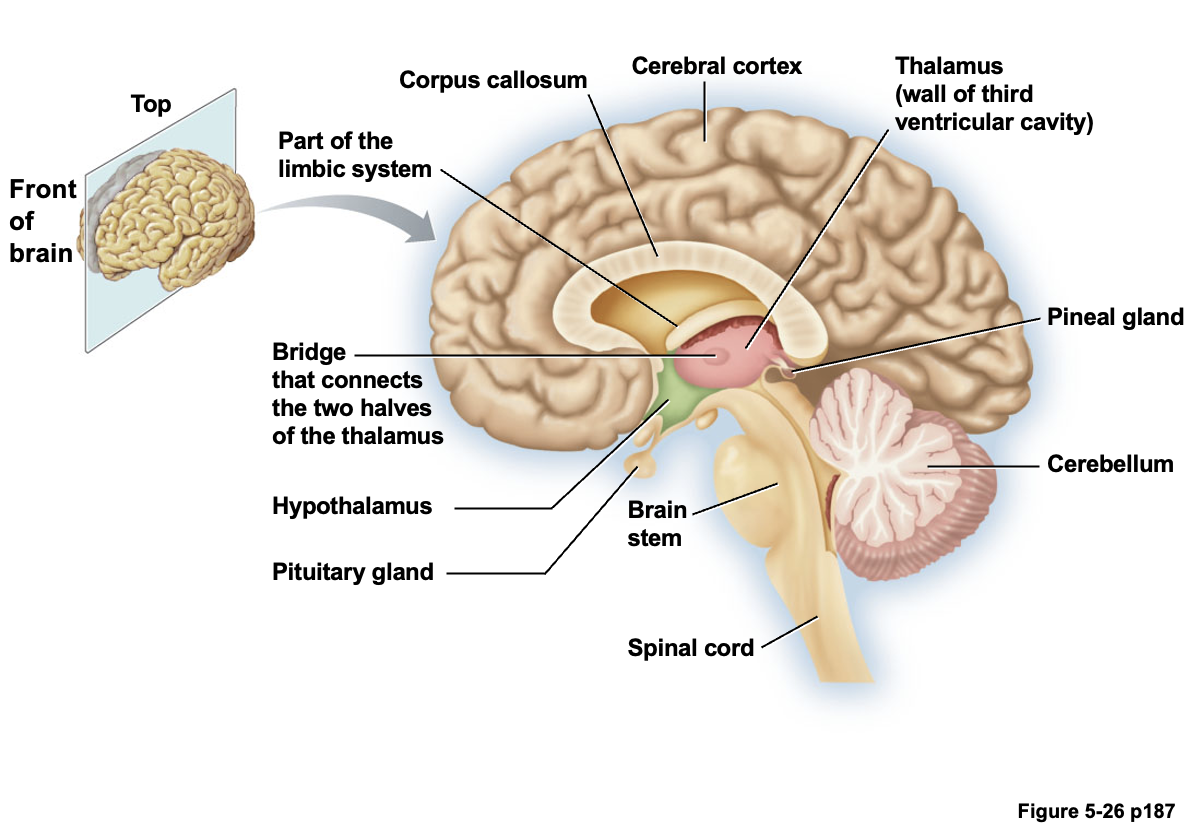
Limbic system 변연계
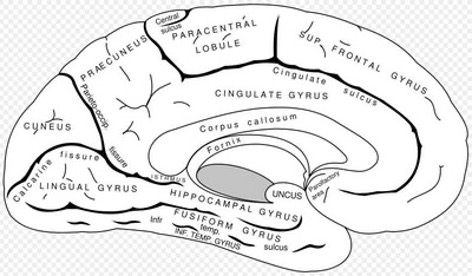
Limbic system plays a key role in animal motivation and memory
Limbic system is not a separate structure
Ring of forebrain structures that surround the brainstem (Fig. 5-27)
Emotion, basic survival, sociosexual behaviour, motivation, learning
Limbic system
Functions
Learning emotional memory
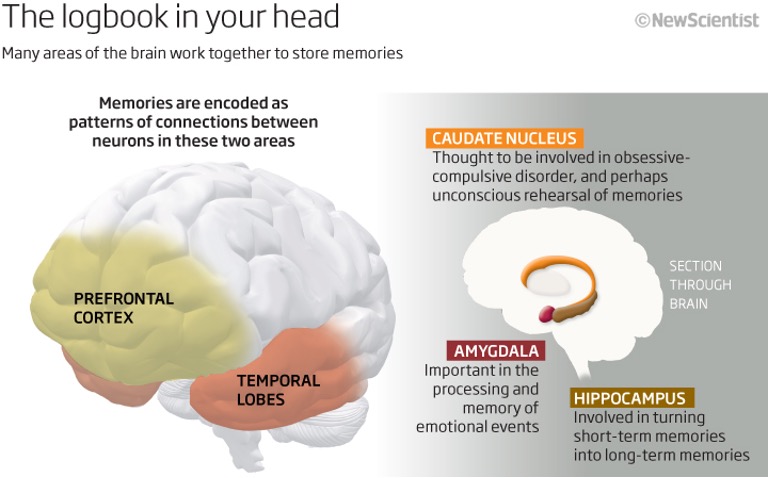
Amygdala
– Processing inputs that give rise to fear for the avoidance of danger
-- A strengthening of synaptic connection in the amygdala are retained for the lifetime
-- Activates the fight-or-flight stress system (that is controlled by the hypothalamus) even before the higher sensory centers perceive the danger -> Previous shock was engraved in synaptic connections in amygdala
-- In the normal condition, GABA has suppressed the fight-or-flight neural circuits in amygdala
Limbic system and higher cortex participate in the control of basic innate behavioral patterns
Different regions of limbic system govern discrete responses against stimuli; especially the hypothalamus is extensively involved
Hypothalamus -> Amygdala -> emotional memory
• Role of the higher cortex in basic behavioral patterns
- Higher cortical mechanisms connect the limbic system (and hypothalamus) with the external environment
- Everyone can smile; Smiling is preprogrammed in the cortex, and called forth by the limbic system
Motivated behaviors are goal directed
Certain regions of the limbic system have been designated as Reward and Punishment centers
Stimulating device implanted rodent Reward center -> Even shun food
Reward centers are found most abundantly in regions mediating eating, drinking and sexual activity
Motivation is the ability to direct behavior toward specific goals
Homeostatic drives represent the subjective urges associated with specific bodily needs that motivate appropriate behavior to be satisfied
Norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin in pathways for emotion and behavior
Functional deficiency of NE or serotonin induces depression
Prozac blocks reuptake of serotonin
Limbic system 변연계
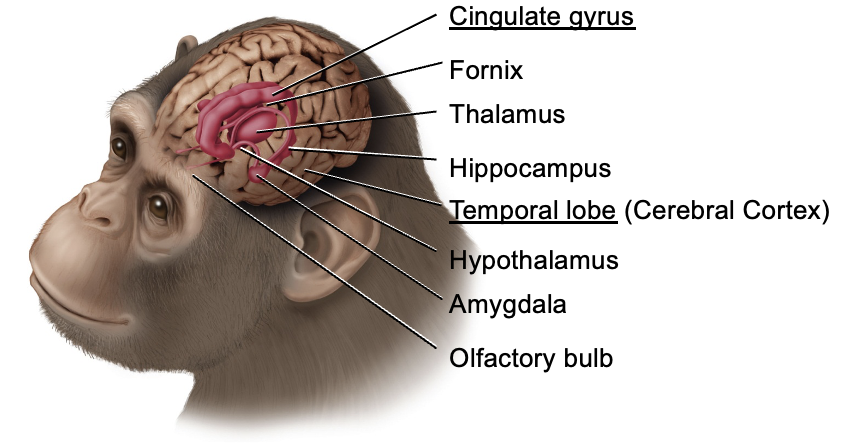
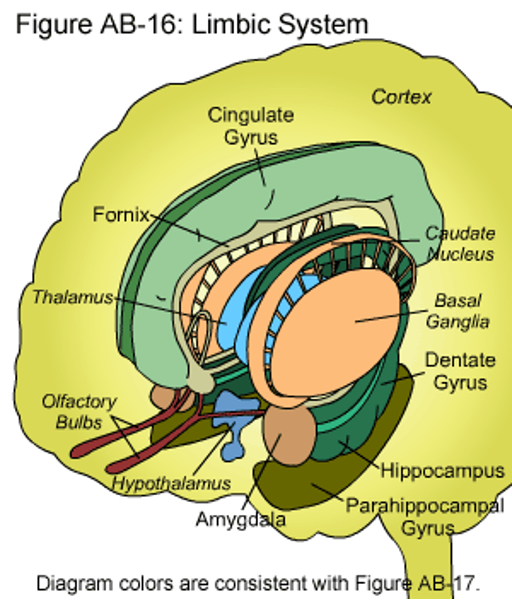
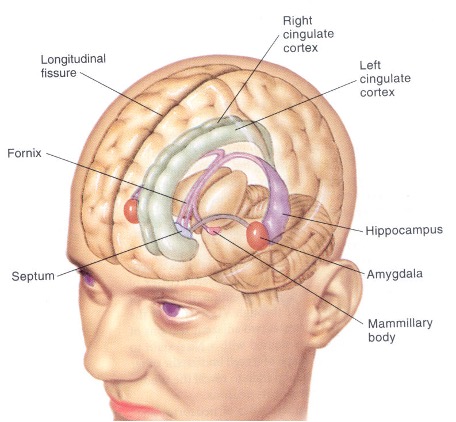
Brainstem을 둘러싸는 cerebrum의 구조물들. 뇌실의 주변을 감싼다. 동물의 감정, 기본적인 생존과 성별에 따른 행동 패턴 결정, 동기 부여와 학습 등에 관여한다. Limbic system은 별도의 구조가 아닌 전뇌 구조의 고리이다.
- Cingulate gyrus : 띠이랑, 대상회전. 정서와 관련된 감정 처리에 관여
- Fornix : 기억을 담당하는 신경 섬유 다발
- Thalamus : 거의 모든 감각 입력을 cerebral cortex로 전달하는 중계소
- Hippocampus : 학습과 기억 형성에 중요한 역할
- Temporal lobe : 언어, 청각 정보 처리, 감정 및 기억에 관여
- Hypothalamus : 신체 homeostasis 유지, 감정, 행동 패턴 및 수면-각성 주기를 조절
- Amygdala : 공포와 같은 감정 처리 및 정서적 기억 형성 관여
- Olfactory bulb : 후각 정보 처리
공포를 유발하는 input을 처리하여 위험 회피를 돕는다. 시냅스 연결 강화를 통해 기억이 평생 유지될 수 있다. 또한, 고위 감각 센터가 위험을 인식하기 전에 이미 fight or flight 스트레스 시스템을 활성화한다.
Limbic system과 고위 cerebral cortex가 외부 환경과의 상호 작용을 통해 행동을 조절한다. 예를 들어, 모든 사람이 웃을 수 있는 것은 cerebral cortex에 사전 프로그래밍되어 있고, limbic system에 의해 불러 일으킨 것.
동기부여 행동
특정 limbic system 영역이 보상 및 처벌 센터로 지정되어 있다. 보상 센터는 주로 먹기, 마시기, 성적 활동 등을 매개한다. 동기 부여는 특정 목표를 향한 행동을 유도할 수 있는 능력이고 항상성 드라이브는 특정 신체적 필요와 관련된 주관적인 충동을 나타낸다. 적절한 행동을 자극하게 된다.
관련된 신경전달물질
- NE(노르에피네프린), Dopamine, Serotonin이 중요한 역할 수행
- NE 또는 Serotonin의 기능적 결핍은 우울증을 유발할 수 있다.
- Prozac은 serotonin의 재흡수를 차단하여 우울증 치료에 사용된다.
'BIOLOGY > Animal Physiology' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Endocrine system (0) | 2024.06.18 |
|---|---|
| [스압 주의]기말고사 특집. 기관 이름 암기 노트 - 의대생 체험 코너 (0) | 2024.06.16 |
| Nervous systems 뇌 시리즈 (1) | 2024.06.15 |
| Neuron system, Sensory physiology 용어 모음집 (0) | 2024.06.15 |
| Homeostasis and Integration : The Foundations of Physiology (2) (0) | 2024.03.21 |

나의 성장 드라마
포스팅이 좋았다면 "좋아요❤️" 또는 "구독👍🏻" 해주세요!

![[스압 주의]기말고사 특집. 기관 이름 암기 노트 - 의대생 체험 코너](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R750x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https%3A%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdn%2FrTeoB%2FbtsH19fa42x%2FBVnFohUpOPa5Cl7hSRb7i0%2Fimg.png)
